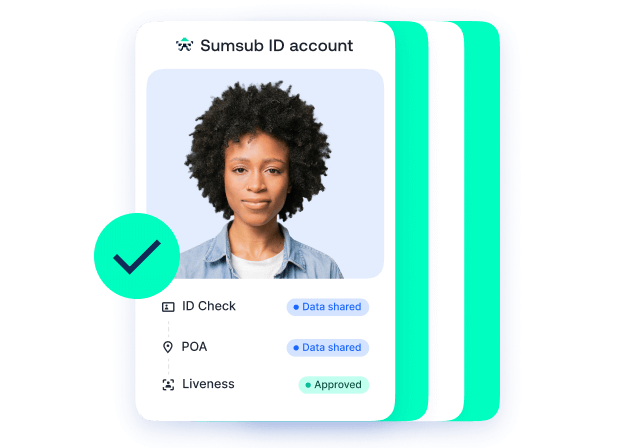
What India, Singapore, and Louisiana Get Right About Digital Identity
In this post, Daniel Flowe, Head of Digital Identity at LSEG Risk Intelligence, explains how digital IDs are transforming interactions with various services through 3 different places around the world.