OCR: How To Extract Information From IDs (2024)
What is OCR and how can businesses use it to speed up their KYC routine?
What is OCR and how can businesses use it to speed up their KYC routine?
For many businesses, Know Your Customer (KYC) checks are an expensive, resource-intensive, and error-prone process, often requiring manual intervention. Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology can help address this issue.
In this article, we’ll explore how OCR works and how it can help digitize verification in banking, fintech, and other industries.
Processing IDs can be challenging for businesses, especially if they operate globally. During onboarding, businesses not only have to validate documents, but also extract identity information for further analysis. Processing this data can be burdensome because:
Images by Sumsub design team
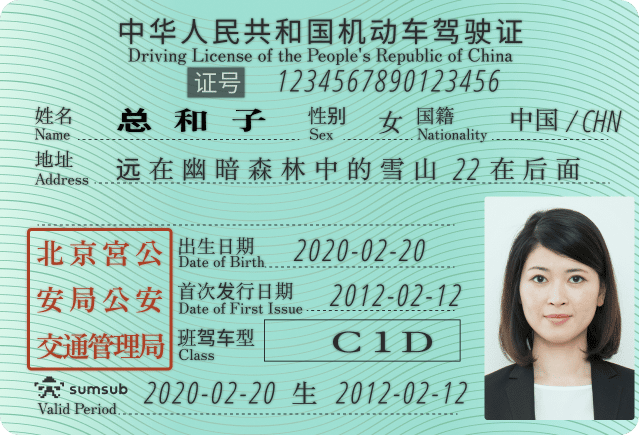
Image by Sumsub design team
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is a technology that converts images of text into editable and searchable data. It’s widely used to digitize books, automate data entry, process invoices, and convert handwriting into digital text. Modern OCR systems use machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI/ML) to improve accuracy, even for complex fonts or handwriting. The technology can also recognize multiple languages and process structured or semi-structured documents.
Suggested read: Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Fraud Detection and Anti-Money Laundering Compliance
OCR works by analyzing the shapes of characters and matching them with a stored database of character patterns. In terms of KYC, OCR scans IDs and extracts user data in a format that is optimized for analysis and electronic storage. This is done by:
OCR can also translate texts containing non-latin characters into Latin during the scanning process. This standardizes data uploaded to the dashboard and prepares it for further analysis.
OCR technology plays a crucial role in identity verification by enabling the automatic extraction and digitization of information from identity documents, such as passports, driver’s licenses, and ID cards. By converting the printed or handwritten text on these documents into machine-readable data, OCR facilitates quick and accurate verification processes, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors. This technology is particularly valuable in remote onboarding and KYC (Know Your Customer) procedures, where it allows businesses to verify identities in real-time by cross-referencing extracted data with official records.
Suggested read: Documentary vs Non-Documentary Verification (2024)
By using OCR in their KYC routine, businesses can reduce costs, save time, and improve the user experience. This includes:
Using OCR to extract data from ID documents eliminates human error and other safety risks, contributing to proper AML/KYC compliance.
OCR can extract data from any type of identity document, including passports, ID cards, driving licenses, residence permits and others. This includes:

Example of OCR extracting data from an ID card
Businesses should consider four criteria for proper OCR:
To fully benefit from OCR technology, businesses should integrate it with their AML and data protection compliance programs.
Sumsub provides businesses with the ability to automatically extract data from any documents with our in-house OCR.
With Sumsub’s OCR, businesses can recognize:
Moreover, Sumsub’s OCR recognizes multiple alphabets and writing systems, including Latin, Cyrillic, Greek, Armenian, Japanese, Korean and Chinese.
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) converts printed text into digital text, while ICR (Intelligent Character Recognition) specifically recognizes and digitizes handwritten text.
Passport OCR extracts and digitizes information from passports, such as name, passport number, and expiration date.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) converts text into digital form, whereas Optical Character Verification (OCV) ensures that the recognized characters match expected values or formats for quality control purposes.