- Jul 01, 2025
- 8 min read
KYC Verification: Full Guide to Know Your Customer Compliance (2025)
Everything you need to know about the #1 defense against fraudsters and money launderers.

Know Your Customer (KYC) is the first and most essential line of defense for online businesses. Failing to implement effective verification measures can allow criminals to infiltrate your platform and may lead to substantial fines from regulators.
In 2024, the UK’s Financial Conduct Authority fined Starling Bank £28.9 million ($39.3 million) for serious AML compliance failures, including insufficient KYC processes during a period of rapid customer growth. This case highlights the critical need for a robust verification system, and also emphasizes the importance of staying updated on evolving AML regulations, which become increasingly stringent each year due to the rising incidence of fraud.
Let’s explore what KYC involves, its types and stages, and the key global regulations you need to follow to stay compliant.
What is KYC?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is the process of identifying and verifying customers. Identification means gathering a customer’s personal data; verification means checking that this data is accurate.
To identify a customer, businesses usually need the following data:
- Name
- Date of birth
- Address
To verify this data, businesses can follow a document-based verification approach. This involves checking the customer’s identity documents and proof of address (usually a utility bill), confirming that they are authentic and valid.
However, more recently, a number of countries have also adopted non-document verification as a compliant KYC method. The solution provides functionality that extracts and verifies comprehensive customer data from government databases, rather than physical documents.
Suggested read: KYC and AML—Key Differences and Best Practices (2024)
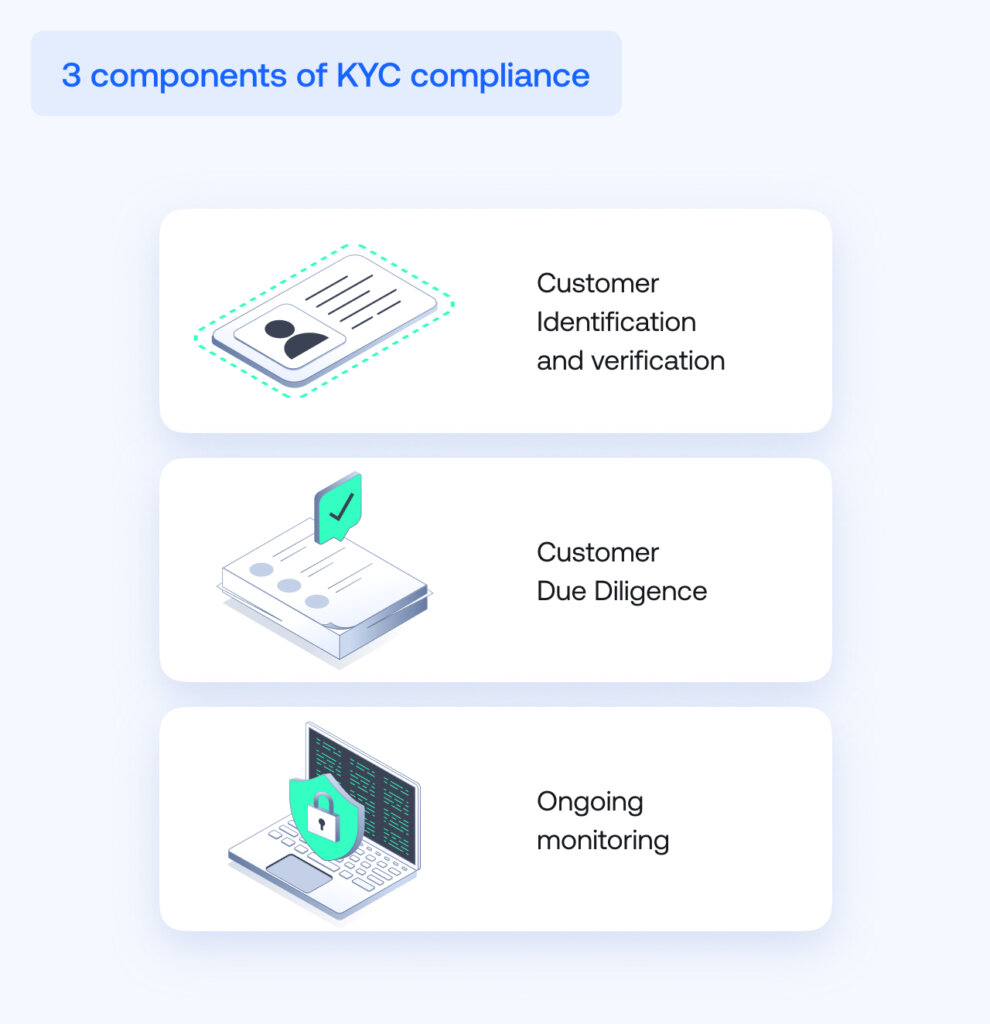
Key components of KYC compliance
KYC consists of several steps that are essential for any company to stay compliant. Let’s dive into them.
- Customer identification and verification
The first step of the KYC process is gathering information and verifying customer data. During this step, relevant documents are collected and their information is compared against information provided by the customer.
Client identification in the US. In the US, financial institutions are required to conduct a Customer Identification Programs (CIP), which is part of the BSA/AML compliance program. This is a US regulation requiring financial institutions to verify their customers during onboarding and transactions. CIPs went into effect as part of the USA PATRIOT Act in 2003 to confront money laundering and terrorism financing.
You can learn more about CIPs at our complete guide on the topic here.
- Customer Due Diligence
CDD, or Customer Due Diligence, aims to pinpoint the customer’s risk profile. To do this additional information is gathered about the customer’s financial history, business activities, and purpose of transactions.
You can learn more about CDD by checking out these articles:
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): The Process and Its Types
- Enhanced Due Diligence: Guidelines and Checklist
- Ongoing monitoring
Ongoing AML monitoring is used to assess a customer’s risk level on a continuous basis (not just at the onboarding stage).For instance, it may involve checking updates to sanction lists and watchlists across the globe to ensure that existing clients haven’t landed on them.
In addition to reactive or manual checks, periodic reviews help with automated, rule-based re‑checks of applicants at configurable intervals. This means that identity, transaction behavior, and risk profile remain up to date throughout the customer’s lifecycle, with minimal manual effort and maximum regulatory compliance.
Types of KYC: Traditional, digital, non-doc, NFC, video, and automated KYC
Not all KYC procedures are created equal. Let’s discuss how customer verification can differ.
Traditional KYC
Traditional KYC typically involves in-person identity verification with physical documents, often requiring a visit to a bank or office.
Digital KYC and eKYC
Digital KYC and eKYC (electronic KYC) are often used interchangeably, but there can be subtle differences depending on the context and jurisdiction. Both are the processes of verifying a customer’s identity online using different methods, e.g. scanned documents, selfies, and other digital data. Digital KYC eliminates the need for in-person verification, making onboarding faster and more accessible.
Document-free verification
Additionally to a standard document-based approach, instead of relying on physical documents, companies verify a user’s identity by accessing government-backed digital ID databases, such as India’s Aadhaar. Authentication is typically completed through biometrics or one-time passwords (OTP), enabling fast, real-time onboarding. This method is especially common in countries with centralized identity systems and strong digital infrastructure and is increasingly used by businesses that need to onboard global users at speed.
Suggested read: Documentary vs Non-Documentary Verification (2025)
Digital identity
Digital identity is an alternative method to verify one’s identity. It is the online or electronic representation of a person or organization’s identity, created through digital attributes and credentials that can be used to authenticate, verify, and authorize someone in digital environments.
Suggested read: Digital Identity in 2025: The Complete Guide
Sumsub offers a Reusable Identity solution, which combines Sumsub ID and Reusable KYC to simplify the KYC process for both users and businesses. With Sumsub ID, users can securely store their verified documents and personal data. Reusable KYC allows companies within the Sumsub ecosystem to access this verified information—with the user’s consent—eliminating the need for repeated checks. The result is faster user onboarding and higher conversion rates for businesses.
Video KYC
Video KYC involves a live video call with a compliance officer who verifies the customer’s documents and identity in real time. It adds a human layer of verification while still maintaining the convenience of remote onboarding. In some jurisdictions, video KYC is an obligatory compliance measure, examples are Estonia and Germany.
Suggested read: The Essential AML/KYC Guide to Germany (2025)
Automated KYC
Automated KYC involves ML/AI-algorithms to instantly check documents, detect fraud, and ensure compliance without human intervention. It’s scalable, efficient, and ideal for businesses processing high volumes of verifications.
NFC verification
NFC (Near Field Communication) verification scans secure identity chips embedded in passports or national ID cards to instantly extract and verify user data. This method offers fast, reliable, and near-impossible-to-spoof verification, making it ideal for high-trust onboarding flows.
How does the KYC process work?
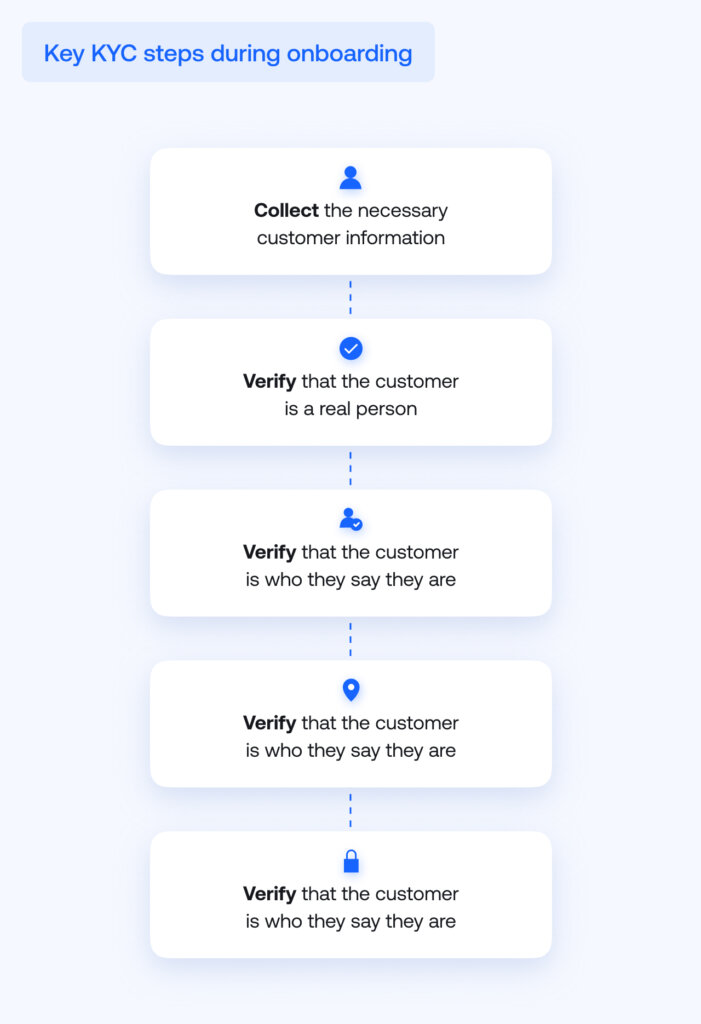
The purpose of the KYC procedure is to verify that a customer is who they say they are. Here’s an example of proper KYC steps, in order:
- Identification—requesting that the customer provides their personal data (name, date of birth, address).
- Liveness check—verifying that the customer is a real and living person. This can be done through facial biometrics authentication.
- Verification—checking that the customer is who they say they are. This includes determining that the customer’s documents are authentic and current. This step may include AML screening to check whether the customer is absent in adverse media, sanctions lists, PEP lists, etc.
- Address verification—verifying that the customer actually resides in their selected country by checking utility bills, bank statements, or other proof of address documents. This includes checking whether the customer comes from high-risk countries (Iran and North Korea) or countries under increased monitoring.
- Risk scoring—determining the risk category of the customer based on the results of the above checks. Depending on the calculated risk level, businesses can adjust their approach to the customer’s verification. Accordingly, a higher risk score will necessitate additional checks.
However, KYC checks don’t end after the onboarding stage. Under AML regulations, businesses are obliged to continue monitoring customers and transactions. This includes checking that documents haven’t expired and detecting suspicious transactions.
Check out Sumsub’s documentation for detailed instructions on how to pass KYC.
KYC requirements for industries
Since KYC falls within AML requirements, any AML-obliged business must perform KYC procedures. Typically, these are financial institutions, crypto businesses, and gambling platforms.
However, customer identity verification is also a highly recommended practice for non-regulated industries such as transportation and e-commerce. In 2025, fraudsters and money launderers are targeting all sectors. This makes a reliable, AI-powered KYC provider essential.
Click on the links to learn more about KYC compliance by industry.
- Banking
- Neobanks
- Fintech
- Forex (binary options)
- Electronic payments
- Crypto (NFT, token sales and ICOs)
- Trading
- Gambling and betting
- Art dealership
- Real estate
KYC regulations around the globe
While many jurisdictions share similar requirements for customer identification and verification, the specific list of mandatory KYC checks can vary. Global regulations are also continuously evolving, with a clear trend toward stricter AML/KYC standards—driven by technological advances, heightened regulatory scrutiny, and the need to combat emerging risks such as digital fraud and the rise of crypto assets.
For example, the key developments of KYC regulations in Europe include:
- EU AML Authority (AMLA), which harmonizes KYC/AML enforcement and fines across member states.
- 6th AML Directive (6AMLD) and new AML Regulation (AMLR) which require stricter beneficial ownership checks and risk scoring.
In APAC, Singapore and Hong Kong tighten rules for Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs), mandating robust KYC. India has updated KYC with geotagged video verification and easier onboarding for foreign investors.
Learn about AML requirements and building KYC processes in the following jurisdictions:
- USA
- Canada
- Australia
- UK
- France
- Germany
- Latvia
- Lithuania
- Hungary
- India
- Malaysia
- Philippines
- Indonesia
- Hong Kong
- CIS
- UAE
- Israel
What is business verification?
Know Your Business (KYB) is all about making sure the companies you work with are legitimate. It involves verifying a business’s structure, ownership (including who really benefits—the UBO), and what it actually does. KYB helps uncover shady setups that might be hiding fraud or money laundering, giving you a clearer picture of who you're partnering with and why.
Check out this detailed guide to learn the steps of the KYB check: KYB (Know Your Business) Verification Guide of 2025
Best practices for 2025 KYC compliance
2025 is marked by harmonized, technology-driven, and risk-adaptive KYC regulations across major regions. The focus is on automation, continuous monitoring, and expanding KYC obligations beyond traditional banking, with steep penalties for non-compliance and a strong push for beneficial ownership transparency. To stay ahead, businesses are encouraged to adopt the following best practices.
- Embrace AI/ML and automation for onboarding and ongoing monitoring
Use AI-powered solutions to streamline customer onboarding and spot suspicious activity faster. Automation reduces manual errors and enhances compliance efficiency.
- Adopt biometric and behavioral analytics for identity verification
Use biometric and behavioral signals like typing speed or device usage to verify users more accurately. These tools make it harder for fraudsters to fake identities.
- Use device intelligence
Device intelligence enables businesses to seamlessly integrate fraud detection capabilities into their applications by combining proprietary solutions with third-party providers (primarily Fingerprint). It helps detect and prevent fraudulent activity within business systems, creating a safer and more secure environment for users.
- Implement perpetual KYC and agile compliance workflows
Shift from static, one-time checks to ongoing KYC that updates as risk profiles change. Agile workflows allow compliance teams to adapt quickly to new threats and regulations.
- Automate sanctions and PEP screening, with frequent data refreshes
Automated screening ensures that politically exposed persons (PEPs) and sanctioned individuals are flagged instantly. Regular database updates help stay compliant with global watchlists.
- Prepare for stricter audits and higher fines by maintaining robust, auditable KYC records
Keep detailed, well-organized records of your KYC processes to withstand audits. Strong documentation can prevent regulatory penalties and build trust with partners.
- Utilize automated periodic reviews
Periodic reviews help make sure that customer information stays accurate and up to date over time. Regular re-assessments support ongoing due diligence requirements and help to stay compliant by flagging potential changes in risk or behavior. This kind of ongoing Due Diligence can automatically trigger full or partial reverification based on customer risk score, elapsed time, or specific triggers.
How to choose a KYC software
The best advice is to choose a solution that covers all the KYC needs of the business in one place, rather than using a combination of different solutions.
Here’s the key criteria for choosing a KYC provider:
- Compliance. The solution must be compliant with the regulatory requirements of the business’s jurisdiction(s). So, if the business is registered in Austria, its KYC provider must be able to conduct video interviews in accordance with Austrian regulations.
- Fraud prevention. Providers should offer strong AI-powered anti-fraud protection that detects forgeries, spoofing, and other malicious activity.
- Flexibility. Businesses should be able to create customizable verification flows for different products and customers.
- Coverage. This means support for document types from different countries.
- Language support. The solution should have different languages for its interface, as well as OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology that can recognize non-Latin characters, such as Chinese, Japanese, or Cyrillic scripts.
- Speed. The solution should have short processing times and high verification speed, so users won’t need to wait long before being verified.
A good set of KYC checks should include:
- Document verification
- Liveness
- Proof of address
- Video identification (depending on the jurisdiction)
- Anti-money laundering checks (AML)
- Customizable verification flows
- Document pre-checks
- Face authentication
- Periodic reviews
It should be noted that KYC is often not enough to stop the spread of fraud. According to our internal research, 70% of fraud takes place after the initial verification. Therefore, when choosing a provider, companies shouldn’t just focus on KYC; they should keep the entire customer lifecycle in mind as well.
FAQ
-
What is full KYC verification?
Full KYC verification involves collecting and verifying a customer’s identity documents, proof of address, and other relevant information to confirm their identity and assess risk. It also includes ongoing monitoring of the customer activity throughout the whole customer lifecycle.
-
KYC vs AML: What’s the difference?
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a component of AML (Anti-Money Laundering) focused on verifying customer identities, while AML encompasses a broader framework of laws and procedures to detect and prevent financial crimes.
-
What documents are required for KYC?
Typically, KYC requires a government-issued ID (like a passport or driver’s license) and a proof of address (such as a utility bill or bank statement). However, the exact set will depend on the jurisdiction and industry.
-
What is KYC in banking?
In banking, KYC is the process of verifying a customer's identity and assessing risk before providing financial services, helping prevent fraud and comply with AML regulations.
-
How do you verify businesses?
To verify businesses (conduct KYB), financial institutions collect company registration documents, ownership structure, and UBO (Ultimate Beneficial Owner) details, often combined with identity checks of key individuals.
Relevant articles
- Article
- 1 week ago
- 6 min read
What counts as proof of address in the UK? See accepted documents and how to open a bank account if you’ve just moved to the country.
- Article
- Feb 5, 2026
- 20 min read

What is Sumsub anyway?
Not everyone loves compliance—but we do. Sumsub helps businesses verify users, prevent fraud, and meet regulatory requirements anywhere in the world, without compromises. From neobanks to mobility apps, we make sure honest users get in, and bad actors stay out.


