- Aug 22, 2024
- 5 min read
Biometric Authentication—Benefits and Risks (2024)
Learn about biometric authentication, modal biometrics, deepfakes, and more.
Biometric authentication is the process of identifying a person by checking one or more of their unique physical characteristics. This process is considered one of the most secure methods of identification due to its high level of accuracy and ability to ensure the person’s presence. Biometrics are therefore used to prevent various forms of crime such as identity theft, account takeover, and transaction fraud.
Cyber attacks are increasing worldwide, with Cybersecurity Ventures estimating that global cybercrime will amount to 10.5 trillion USD per year by 2025.
It’s therefore crucial for businesses to verify user identities accurately—and biometric authentication technology is answering the call. However, biometrics do have their risks. So let’s explore how biometrics work for authentication and evaluate the pros and cons.
What is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication involves verifying a person's identity by analyzing one or more of their distinctive physical traits (e.g. facial recognition, fingerprints, voice recognition, etc).
Because of its full-proof advantages, biometrics are used as a form of identification everywhere, from unlocking smartphones, accessing secure facilities, authorizing financial transactions, and ensuring secure access to computer systems.
Biometric authentication is often confused with biometric verification, but there are still slight differences. Check out this article to learn more, including the details of biometric verification systems.
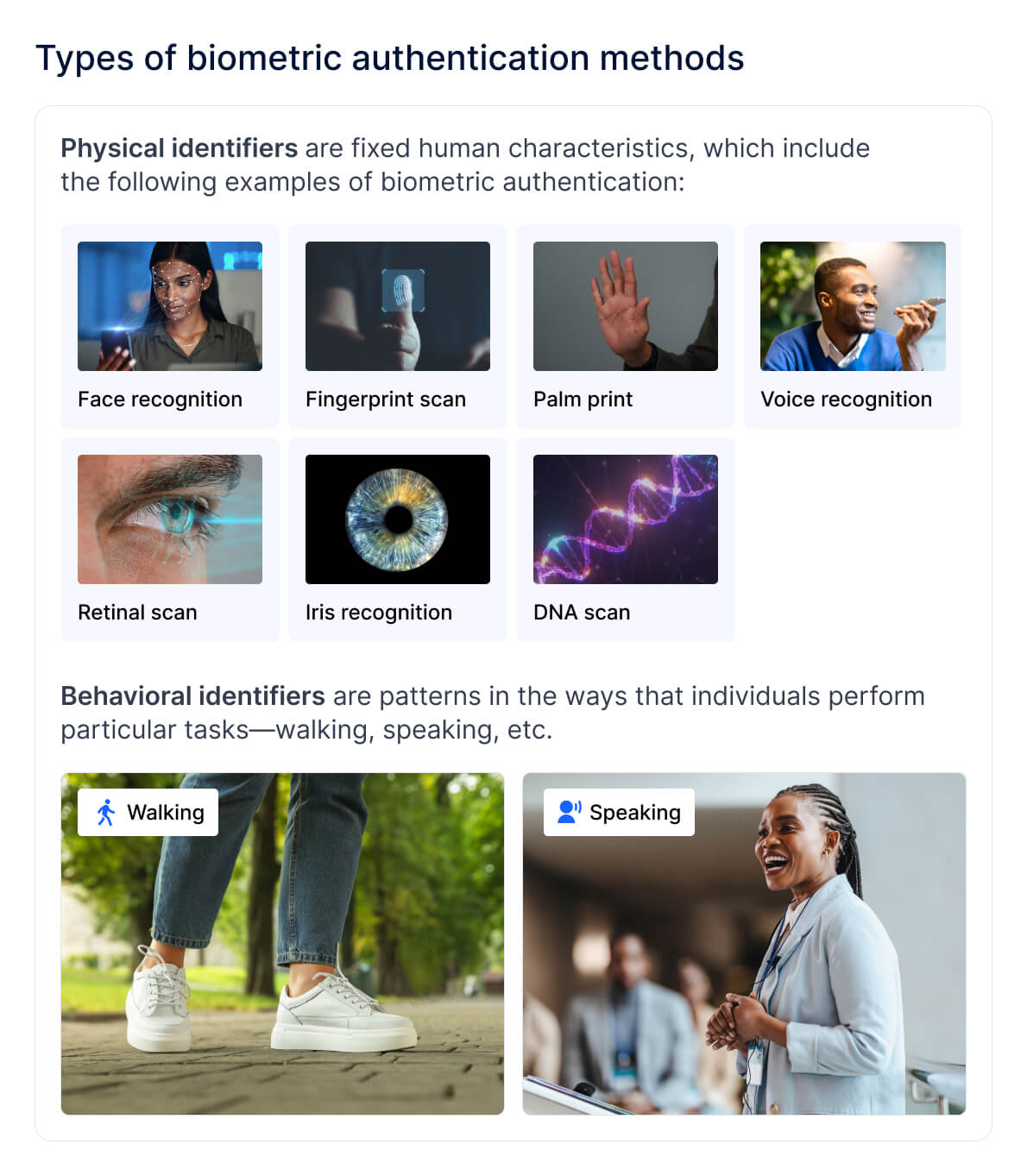
Types of biometric authentication methods
Biometric authentication methods include physical and behavioral identifiers.
Physical identifiers are fixed human characteristics, which include the following examples of biometric authentication:
- Face recognition—a technology which identifies and measures a human face. It is an increasingly popular approach among online services, often used on smartphones.
- Fingerprint scan—a technology which recognizes and verifies the fingerprint of an individual. It is the most common type of biometric authentication, which is also deployed on smartphones.
- Palm print—a technology which examines the unique patterns of veins and lines on the palm, as well as hand geometry (the shape and size of a person’s hand).
- Voice recognition—a technology which identifies a person based on their unique voiceprint. It is used by telephone-based and digital service portals to authenticate customers.
- Retinal scan—a biometric technique using a flashing UV light which passes through the person’s retina blood vessels and creates an image code. It is considered to be 20,000 times more accurate than fingerprints, and is commonly employed for medical purposes.
- Iris recognition—captures the iris pattern in the human eye. It’s considered one of the most accurate types of biometric identification, and is faster and less intrusive than a retinal scan.
- DNA scan—uses genetic material to identify a person and is commonly used by law enforcement to identify suspects.
Behavioral identifiers are patterns in the ways that individuals perform particular tasks— walking, speaking, etc.
Multimodal biometric authentication
Multimodal biometric authentication, also known as multimodal fusion, refers to the practice of combining two or more distinct biometric traits to verify the identity of an individual.
By utilizing several biometric factors, multimodal biometric systems aim to enhance accuracy and security while mitigating the limitations associated with using a single biometric trait.
In a multimodal biometric authentication system, two or more biometric modalities are simultaneously captured and processed to complete authentication. The combination of modalities can be used to overcome the weaknesses of individual biometric traits and improve overall system performance.
Moreover, the likelihood of false positives or false negatives is reduced when multiple biometric traits are used in conjunction.
Advantages of biometrics over traditional authentication methods
Biometrics are preferable to passwords, PINs, or security tokens because they’re easier to use and provide greater privacy and security. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Strong security and lower risk of identity theft. Biometric traits are unique to each person, and are difficult to replicate, which makes it harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Non-transferable features. Biometric traits are tied to a person and can’t be easily transferred or shared. In contrast, passwords and PINs can be shared or stolen.
- Convenience. Biometric authentication eliminates the need to remember and manage passwords, reducing the risk of forgotten or weak passwords. Users can simply use their natural biometric features to authenticate.
- Improved UX. Biometric authentication is usually quick, reducing the time and effort required to access devices or services, which makes the user experience more pleasant.
- Low risk of human error. Biometric authentication minimizes the potential for human error (such as misprints when entering passwords or occasionally sharing passwords/credentials via emails or messages, etc.) during the authentication process.
- Multi-factor authentication. Biometric methods can be used as part of multi-factor authentication (MFA), where multiple authentication factors are combined for stronger security.
- Wide range of characteristics. Biometric authentication can utilize a wide range of characteristics, including physical (fingerprint, face, iris) and behavioral (e.g. typing pattern) traits, providing flexibility and options for different use cases.
- Future-proofing. Biometric traits remain relatively stable throughout a person's life, reducing the need for frequent updates or changes to authentication methods.
Despite these advantages, biometric authentication does come with a number of challenges.
Risks
Some of the potential risks associated with biometric authentication include:
- Appropriate technical and organizational measures. Biometric data is highly personal and unique to each individual. Thus, the processing of biometric data requires special security and organizational measures to ensure an appropriate level of data security.
- Data breaches. If biometric data is compromised, it can’t be changed like a password. Once biometric data is stolen, it is permanently compromised, potentially leading to identity theft or unauthorized access.
- False positives and negatives. Biometric systems can occasionally produce false positives (incorrectly authenticating an unauthorized person) or false negatives (failing to authenticate an authorized user). These errors can impact both security and user experience.
- Forgery. Some biometric systems can be fooled by high-quality replicas or "spoofs" of biometric features, such as fingerprints or facial features. This can be a photograph, 3D model, or silicone fingerprint replica used to bypass certain biometric security measures. Therefore, it is essential to use advanced biometric technology which is capable of recognizing even the most sophisticated deepfakes.
- User apprehension. Some individuals may be uncomfortable with providing their biometric data due to privacy concerns, cultural reasons, or personal preferences. This can lead to adoption challenges.
- Regulatory compliance. Collecting, storing, and using biometric data may be subject to regulatory requirements and legal frameworks that vary by jurisdiction. Companies need to thoroughly examine these complexities to ensure compliance.
- Longevity of biometric features. While many biometric traits remain relatively stable over an individual's lifetime, some may change due to aging, injury, surgery, or other factors. This can lead to issues with authentication accuracy.
To overcome these challenges, biometric authentication should be used carefully, implement strong security practices, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations. Additionally, using multi-factor authentication (MFA), which combines biometrics with other authentication factors, can provide an extra layer of security.
Use cases
Biometric authentication has a wide range of use cases across different industries and sectors, for example:
- Identification and verification as part of Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures and AML compliance in various industries, particularly in the financial sector.
- Multi-factor authentication using biometrics for extra security. MFA combines something the customer knows (a PIN or a password), something they have (a mobile device), and their biometric traits.
- Prevention of account takeovers. This is especially relevant for industries like carsharing, payments, banking, and crypto.
- Prevention of promo abuse fraud. Thanks to a biometric check that matches new account data with existing customer profiles, business owners can be sure that offers and special pricing plans go to first-time users only. This is especially relevant for gaming, streaming services, and delivery services.
- Prevention of arbitrage betting.
- Prevention of multi-accounting. This is relevant for all peer-to-peer services, as well as e-commerce and gaming, streaming services and online education platforms, when students try to share one account to avoid paying for the service—or, worse, cheat on exams.
- Securing physical entrances. Biometrics can be used to control access to doors, gates, and other entry points.
Suggested read: Combating Multi-Accounting: How Sumsub Can Help the Most Affected Industries
Biometric authentication and deepfakes
According to Sumsub’s 2023 Identity Fraud Report, there has been a tenfold increase in the number of deepfakes detected globally across all industries from 2022 to 2023, with notable regional differences.
Biometric authentication can play a significant role in combating the threats posed by deepfakes. Here’s how:
Liveness Detection:
Liveness detection verifies that biometric data is extracted from a live person, not a static image or video. By analyzing natural movements, liveness ensures real-time presence, effectively countering deepfake attempts that use manipulated media. Sumsub’s Liveness Detection solution uses AI algorithms which can easily spot enhanced images.
Behavioral Biometrics:
Behavioral biometrics track patterns like typing speed and mouse movements to detect anomalies that may suggest manipulation or deepfake usage, enhancing fraud detection capabilities.
Multi-factor Authentication:
Combining biometric authentication with other verification methods, such as one-time passcodes, reduces the risk of successful deepfake attacks.
Suggested read: What Are Deepfakes?
While biometrics can help identify deepfakes in some situations, it should be part of a broader strategy that includes utilizing other AI-driven detection tools and raising public awareness.
FAQ
-
How are biometrics used for authentication?
Biometric authentication identifies a person by assessing one or more of their unique physical characteristics (e.g. fingerprints, iris or retina, voice, face).
-
What is the difference between biometric and fingerprint authentication?
Fingerprint authentication can be part of biometric authentication. Fingerprint authentication specifically involves using the unique patterns of ridges and valleys on an individual's fingertip as a means of identification, while biometrics use a broader range of a person’s traits to ensure that the person is who they claim they are.
-
Can biometrics be used for MFA?
Yes, biometric authentication can be part of multi-factor authentication (MFA).
-
What are the risks of biometrics in cyber security?
Potential data breaches are the biggest risk of using biometrics. If biometric data is compromised, it can’t be changed like a password or a PIN. Once biometric data is stolen, it is permanently compromised, potentially leading to identity theft or unauthorized access.
-
Can biometric authentication be fooled?
Biometrics are harder to bypass or fool in comparison to traditional authentication methods, like passwords. However, some biometric systems can be fooled with advanced deepfakes. Therefore, it’s recommended to use advanced biometric systems supported by other authentication methods for extra security, or multimodal biometric authentication.
-
Is biometric login safer than a password?
Yes, biometric login is safer than using passwords or PIN codes.
Relevant articles
- Article
- 1 week ago
- 11 min read
Check out how AI deepfakes are evolving and discover proven strategies for detecting and preventing deepfake threats to protect your business.

- Article
- 3 weeks ago
- 9 min read
What is Sumsub anyway?
Not everyone loves compliance—but we do. Sumsub helps businesses verify users, prevent fraud, and meet regulatory requirements anywhere in the world, without compromises. From neobanks to mobility apps, we make sure honest users get in, and bad actors stay out.