- Aug 19, 2022
- 4 min read
How to Grow a Successful Forex Platform and Comply with AML/KYC Laws in Different Countries
This article helps FX platforms keep their reputation flawless while avoiding regulatory fines.
Forex trading is more popular than ever. With a traded volume level of more than $4 trillion a day, forex has also become a lucrative target for financial criminals, in turn attracting stricter oversight by regulators.
Just two years ago, US financial regulators FINRA, the SEC, and the CFTC issued fines totaling more than $38 million to Interactive Brokers for “widespread failures” in the firm’s anti-money laundering (AML) program.
To keep reputations flawless and revenues high, all FX businesses need to balance customer onboarding, AML/CTF compliance, and fraud prevention. Sumsub’s legal team is here to help. Below, we’ll go over what forex compliance is all about, detailing the latest regulations and KYC/AML best practices. This will help FX platforms maximize efficiency and avoid harsh penalties for non-compliance.
How is the forex market regulated?
As FX trading is a global activity, there isn’t a single set of forex broker regulations that applies to all platforms (there is the FATF’s Risk-based Approach Guidance for the Securities Sector, but it does not have the force of law). Instead, there are multiple types of requirements, which vary depending on where forex platforms operate. Nevertheless, some of these regulations overlap across multiple jurisdictions—particularly those related to anti-money laundering (AML) and countering the financing of terrorism (CFT).To stay in line with anti-money laundering (AML) regulations, businesses need to enact an AML policy for forex. This includes setting up adequate internal systems for spotting suspicious activity and reporting them to authorities, as well as robust Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures to verify customers and take precautions against money laundering and terrorist financing.
The importance of customer due diligence (CDD) and “know your customer” (KYC)
CDD applies to all procedures that AML-obligated entities use to verify customer identities, background information, and risk levels. When performed correctly, CDD measures identify high-risk individuals at an early stage, preventing companies from being exposed to money laundering, fraud, terrorist funding, and other financial crimes.
When establishing a business relationship with a client, the first (and most important) CDD measure is to perform KYC. This is to ensure that the clients are who they say they are. To do this, businesses obtain key information about the customer (name, address, date of birth, etc.) and verify the accuracy of this information.
However, CDD shouldn’t stop after the KYC stage. Existing customers should also be subject to CDD measures through ongoing monitoring, as customer risk profiles may change over time. Accordingly, businesses should take customer account activity into consideration, in addition to ensuring that all their KYC documentation remains up to date. Record-keeping is also a necessary part of ongoing CDD, helping businesses maintain a clear understanding of their customers throughout the entire lifecycle.
In unison, KYC and ongoing CDD help businesses prevent—or promptly react to—crises stemming from fraud and money laundering attempts.
Absent or inadequate CDD and KYC procedures can subject businesses to serious reputational, operational, and legal risks. Regulators around the world heavily penalize entities that don’t adhere to AML standards, fining banks, large multinational corporations, and forex firms at record levels (up to $900 million).
Global regulators have identified four key AML failings from 2016-2021:
- AML management,
- Suspicious activity monitoring,
- Customer due diligence,
- Compliance monitoring and oversight.
What is KYC in forex?
KYC is a legal requirement for forex platforms to verify customer identities. The customer data required for collection may vary from one country to the next. However, forex operators usually request the following:
- passport or national ID number, and country of issuance;
- date of birth;
- residential or business address;
- phone number;
- email address;
- sample signatures;
- other financial information, such as the purpose for opening a trading account, source of funds, etc.
This information is usually verified by FX companies using KYC documents, such as passports, national ID cards, utility bills and financial statements.
It is the responsibility of the FX firm to implement account verification and KYC procedures in order to fulfill legal and regulatory obligations.
Check out our KYC Guide for the Trading Industry. It will help you meet compliance requirements and build high-conversion verification flows. Inside, you'll find:
- An overview of trading regulations
- KYC for licensed and non-licensed brokers
- Recommendations for building perfect verification flows

What are the regulations for forex brokers? (List of countries in alphabetical order)
Every forex platform has to comply with the AML/CTF regulations of their jurisdiction. These requirements may differ from country to country, so platforms should take care when choosing the jurisdiction for business registration and brokerage licensing.
Below you’ll find a list of key forex broker regulations, laws, and jurisdictions. Click on each country to learn more.
-
Australia
Legislation:
- Registered AML Rules (Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre);
- Australian Anti-Money Laundering and Counter Terrorism Financing Act 2006;
- Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing Rules Instrument 2007 (No. 1).
Regulating bodies:
- The Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC) regulates forex trading in Australia.
- The Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre (AUSTRAC) is responsible for monitoring the AML compliance of financial institutions. Financial institutions are required to register and enroll their business with AUSTRAC.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identification and verification of individuals: Collect their name, date of birth, and address. Verify the data using document-based or electronic-based approaches.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect the name, addresses of registration and principal place of business, registration number (either their Australian Company Number or Australian Registered Body Number), the nature of the company, and the names of the directors. Only the name, legal form and registration number must be verified.
Penalties for non-compliance: A civil penalty of up to A$4,4m (~$3,1m) for an individual and up to A$22.2m ($15.3m) for a corporation. Those are the maximum penalties applied, where the penalty unit amount is $222.
*Under the Notice of Indexation of the Penalty Unit Amount, a penalty unit is currently $222. Penalty units are used to calculate fines for various offenses. Fines are calculated by multiplying the value of one penalty unit by the number of units that offense carries.
-
Belize
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- The International Financial Services Commission (IFSC) regulates forex brokers in Belize.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identifying individuals: Collect their name, address, date and place of birth, nationality, contact details, signature, purpose of the account and the nature of the business relationship.
- Non-face-to-face identification: Take specific and adequate measures to compensate for higher risk. This includes communicating with the customer at an address that has been verified, two-factor authentication, requiring copied documents to be certified, etc.
- Identification and verification of corporate customers: Collect their name, principal place of business and registered office, contact details, board resolution, certificate of incorporation, identities of all account signatories and details of their relationship with the company, identity information on the natural persons with a controlling interest in the corporate entity.
Penalties for non-compliance: A fine of up to $25,000, imprisonment up to 3 years, or both.
-
Bulgaria
Legislation:
- Measures Against Money Laundering Act, 2008, amended in 2018;
- The 4th EU Money Laundering Directive (the new amendments to the law implement the Directive within Bulgarian legislation).
Regulating body:
- The Bulgarian Financial Supervision Commission (BFSC) regulates the forex market in Bulgaria.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identifying individuals and verifying their identities: Collect the name, date and place of birth, personal identification number/unique Identification number of client, nationality, country of permanent residence, and address of the customer.
- Identification and verification of the legal entities: Collect basic information on entities, legal persons. Establish the corporate structure, identifying and verifying the natural persons that directly or indirectly control the company.
Penalties for non-compliance: A fine ranging from $300-$3,000 for individuals, $600-$6,000 for legal entities. The penalties are to be applied monthly until the requested information is duly registered.
-
Cyprus
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC) is the financial regulatory agency of Cyprus that oversees and provides licenses to forex brokers.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identifying individuals and verifying their identities: Collect their name, address, telephone and fax numbers, e-mail address, signature, date and place of birth, details on their profession and other occupations, including the name of their employer. The customer’s identity shall be verified on the basis of documents, data or information obtained from a reliable and independent source. For non-face-to-face identification, two methods prevail: real-time video selfie or video interview.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect their name, registration number, office address, location of the head or main office, telephone numbers, fax numbers, e-mail address, the members of the board of directors, the persons that are duly authorized to operate the accounts of the company and act on behalf of the company, the registered shareholders, the business profile of the company.
- Specific procedures required by CySEC: Check the adequacy of the data and information pertaining to the customer’s identity and economic profile when:
- an unusual or significant transaction takes place;
- there is a change in the customer’s legal status and situation;
- there is a change in the rules and methods of customer account operation.
Penalties for non-compliance: An administrative fine of up to €200,000 ($235,250). In case the offense continues, an additional administrative fine of up to €1,000 ($1170) is imposed for each day.
-
Japan
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- The Financial Services Agency (FSA) is the main forex broker regulator in the country. To obtain a forex license in Japan, brokers need to follow its guidance.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identifying individuals and verifying their identities: Collect their name, address, and date of birth (has to be verified from valid customer identification documents such as a driving license, passport, or alien registration card), details on their profession and other occupations, purpose of transaction, status of asset and revenue, confirmation of personal identification data of the person in charge of the transaction, confirmation of agency power for the person in charge of the transaction. For higher risk customers, it is also required to verify assets and income.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect their name, location of the head office, the nature of the company, purpose of transaction, and identity of beneficial owner(s). For higher risk customers, it is also required to verify assets and income.
Penalties for non-compliance: A fine of up to ¥3,000,000 ($27,215) for individuals and up to ¥300,000,000 ($2.7m) for legal entities. The maximum penalty is imprisonment of up to two years for responsible persons.
-
Malta
Legislation:
- The Prevention of Money Laundering Act (Chapter 373 of the Laws of Malta);
- The Implementing Procedures, issued in terms of Regulation 17 of the Prevention of Money Laundering and Funding of Terrorism Regulations (PMLFTR).
Regulating body:
- Malta Financial Services Authority (MFSA) is the regulating authority for all forex brokers in Malta. To carry out their activities in Malta, brokers should be authorized by the MFSA.
- Financial Intelligence Analysis Unit (FIAU) is a government agency established under the Prevention of Money Laundering Act. The Unit is responsible for monitoring compliance with AML provisions.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identifying and verifying identity details of natural persons: Collect their name, address, place and date of birth, identity card reference number (where available) and nationality. Verification of the identity details shall be carried out either by referencing government-issued documents containing photographic evidence of identity or other documents bearing a photo of the individual. SoF/SoW check for high-risk customers should be applied.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect and verify through documentation their name, registration number, date of incorporation or registration, and registered address or principal place of business. Establish the corporate structure and verify the beneficial owners.
Penalties for non-compliance: A fine up to €5,000,000 ($5.9m) or the equivalent of 10% of total annual turnover (according to the latest financial statements).
-
Marshall Islands
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- The Marshall Islands have no local forex trading regulatory bodies. However, there are a number of forex brokers in the Marshall Islands that are authorized and licensed by different types of international regulatory bodies, such as CySEC of Cyprus, and others. Therefore, if a company is regulated by CySEC, it must comply with all the requirements set out by CySEC, including its branches.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identification and verification of individuals: Collect their name, address, telephone and fax number, date and place of birth, nationality, details on their profession and other occupations, including the name of their employer, a copy of their passport or national ID, signature, purpose of the account and the potential account activity, written authority to obtain independent verification.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect their certificate of incorporation, articles of association, location of their head office or registered agent, description and nature of their business, board resolution, the names and addresses of all officers, directors, and beneficial owners, confirmation that the corporate entity has not been struck off the register or is not in the liquidation process, purpose of the account and the potential parameters of the account, written authority to obtain independent verification.
Penalties for non-compliance: A civil penalty up to $10,000 per violation for any willful violation of record-keeping; up to $500 per violation for any negligent violation of any requirement.
Jurisdictions generally considered ‘reputable’ are the US, UK, EU, Switzerland, Japan, Singapore, Australia, New Zealand.
When assessing the reputability of a jurisdiction, it is recommended to use trusted sources of information, such as:
-
UK
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) regulates all companies and investors in the field of finance. Thus, all brokers regulated in the UK are obligated to follow their guidelines, otherwise the FCA has the right to revoke their license and impose disciplinary measures against the company in question. You can search their Register for firms and individuals authorized by the FCA.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identification and verification in respect of individuals : Collect their name, photograph on an official document which confirms their identity, residential address and date of birth, along with utility bills, bank statements and other official documents. Other sources for verification of information include the electoral register and information held by credit reference agencies.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect name, location of the office, the nature of the company, purpose of transaction, identity of the beneficial owner.
For higher risk customers, it is also required to verify assets and income.
Penalties for non-compliance: Over £1,000,000 ($1.2m).
-
USA
Legislation:
Regulating body:
- The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) writes and enforces rules governing the activities of all registered brokers in the United States. To conduct securities transactions or any other business with investors in the U.S., both firms and individuals must be registered with FINRA.
Complying with CDD requirements:
- Identification and verification of individuals: Collect their name, date of birth, address, and an identification number (typically a social security number). It is also required to create a customer risk profile and conduct ongoing monitoring.
- Identification and verification of legal entities: Collect their name, principal place of business, office location, or other physical location of operations or presence, identification number, employer identification number (EIN), and beneficial ownership information.
- Verification of identities shall be carried out through documents or non-documentary methods
Penalties for non-compliance: A fine of over $1,000,000.
Anti-money laundering and countering the financing of terrorism legislative package
The EU Sixth Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD)
On July 20, 2021 the European Commission presented a package of 4 legislative proposals to strengthen the EU’s existing anti-money laundering rules. This includes a proposal for the creation of a new EU authority to fight money laundering which should be operational in 2024. It will perform a direct supervisory role once 6AMLD is transposed and the rules kick in.
Main initiatives:
- Creating AMLA – a new EU AML Authority to enhance cooperation of local authorities in ensuring the private sector correctly and consistently adheres to EU rules.
- New regulation on AML/CFT, which will unify EU AML requirements, including CDD.
- Revision of Regulation of Transfer of funds, which will allow trace transfers of virtual assets.
- Establishing the mechanisms that EU member states should put in place to prevent the use of the financial system for ML/TF purposes
Click here to find our practical advice on complying with 6AMLD.
How Sumsub can help
With Sumsub, forex platforms get quick and easy KYC that converts even the least motivated users in minutes. The verification process requires just two photos from the user and takes just a couple of minutes. As a result, the business can increase conversion by 30% or more.
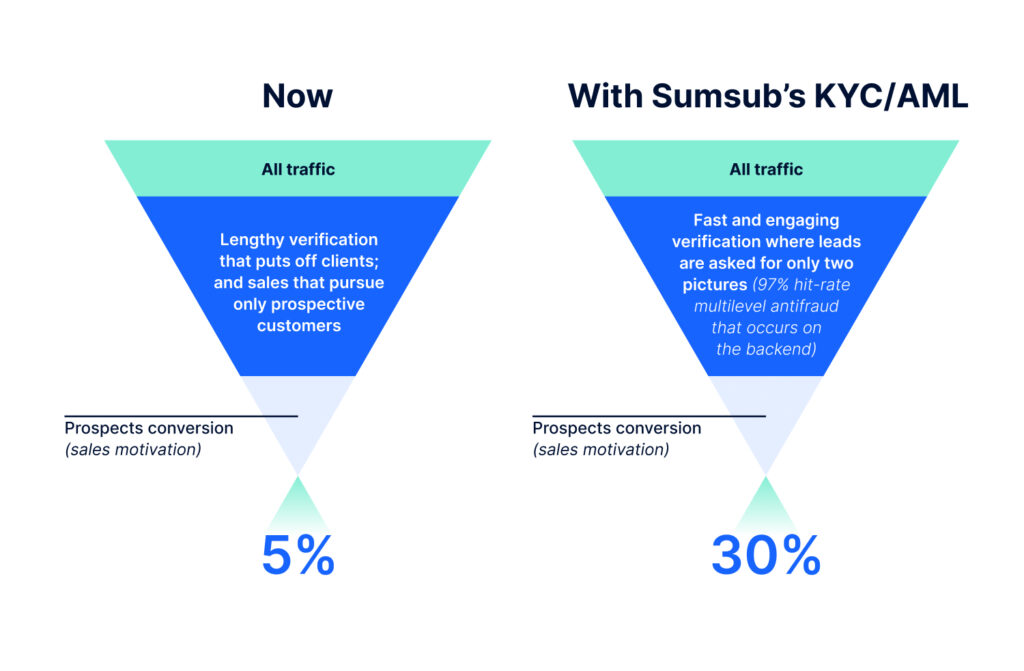
Sumsub’s identity verification platform enables businesses to increase customer conversion, all while ensuring compliance with FX regulations worldwide (ongoing monitoring, record-keeping and so on). The solution is globally applicable, as its approach and methodology are carefully designed according to the latest recommendations on AML and CFT.
The bottom line

As the forex market generates more interest across the globe, scammers become an ever-increasing threat. However, if you put time and effort into implementing professional KYC and AML practices, you’ll minimize the risk of fraud and other dangers. Plus, you’ll be best-equipped to deal with constantly shifting regulations, avoiding steep fines and penalties along the way.
Relevant articles
- Article
- 4 days ago
- 11 min read
Arbitrage in Sports Betting & Gambling in 2026. Learn how iGaming businesses detect arbers using KYC & fraud prevention tools.

- Article
- 3 weeks ago
- 8 min read
AI-generated fake IDs are bypassing traditional KYC: learn why businesses need to rethink their identity verification in 2026.
What is Sumsub anyway?
Not everyone loves compliance—but we do. Sumsub helps businesses verify users, prevent fraud, and meet regulatory requirements anywhere in the world, without compromises. From neobanks to mobility apps, we make sure honest users get in, and bad actors stay out.