- Mar 25, 2025
- 9 min read
Digital Identity in 2025: The Complete Guide
Learn what digital identities are, how to verify them, and what kind of future awaits digital identity.
Our personal information is increasingly stored and shared online—meaning that our digital identity is more valuable than ever—but also more vulnerable to cyber threats, fraud, and identity theft. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) received 5.7 million reports of identity theft and fraud in 2024, up from 4.7 million the previous year. But what exactly is digital identity?
Let’s dive into the specifics in this article: what digital identity is, who has it, and how it can be authenticated.
What is digital identity?
Today, digital identities are the collection of electronic information that uniquely represents an individual, organization, or device in the digital world. This includes personal data like names, dates of birth, email addresses, usernames, passwords, social security numbers, and passport numbers. These identifiers help you access services and interact within digital environments.
How is digital identity different from traditional identity?
Traditional identity is based on physical documents like passports, driver’s licenses, birth certificates, and national ID cards—all documents that prove who you are in the real world. They require in-person verification, which makes identity confirmation a slower, manual process.
Digital identity, on the other hand, exists entirely online. Instead of physical documents, it uses electronic credentials like usernames, passwords, biometrics, and cryptographic keys to verify someone. This allows you to access services remotely—whether it's logging into your bank account, proving eligibility for government benefits, or even crossing borders with a digital passport.
The key difference is how verifying through them works:
- Traditional identity verification often requires face-to-face interaction, such as presenting an ID at a bank or government office.
- Digital identity verification happens online, using AI-powered document checks, biometric scans, or multi-factor authentication.
For example, while a physical passport is required for international travel, many airports now use digital identity solutions like mobile passports or biometric e-gates, which let you verify your identity instantly using facial recognition.
While digital identity is more convenient and scalable, it also introduces new security and privacy challenges, making strong authentication and data protection essential.
Who has a digital identity?
Virtually everyone who engages with digital platforms has a digital identity. This includes people with email accounts, social media profiles, online banking accounts, or any kind of presence on the Internet.
Organizations, applications, and devices also have digital identities, which makes them able to interact securely within networks and various systems.
Digital identities vs accounts: What’s the difference?
It’s easy to assume that a digital identity and an account are the same thing—but they’re not.
A digital identity is a broader concept: it represents who you are online through a combination of identifiers (like your name, email, or biometrics) and credentials (like passwords or digital certificates).
An account, on the other hand, is a specific relationship between a user and a service. It’s created when you sign up for a platform and is typically linked to a username, email, or phone number. It is secured by authentication methods such as passwords or biometrics.
For example, think of your Google account. When you log in to Gmail, YouTube, or Drive, you’re using the same credentials across multiple platforms, but that doesn’t mean your Google account is your digital identity.
Your digital identity includes far more than just your Google credentials—it also consists of your banking logins, government-issued eIDs, social media profiles, and other identifiers that define your presence online.
Some systems look to unify digital identities across platforms, like Single Sign-On (SSO) solutions from Google, Apple, and Microsoft. These allow users to access multiple accounts with a single verified identity, reducing friction and raising security and privacy considerations.
Types of digital identities & identifiers
Digital identities come in various forms, depending on how they are created, used, and verified. These identities are built from different identifiers, which are data points that uniquely distinguish a person, organization, or device in the digital world.
Digital identities are made of a combination of these identifiers, and their security is critical in preventing fraud, identity theft, and unauthorized access. Some digital identifiers include:
- Personal identifiers
These are directly tied to an individual and help prove their real-world identity, such as:
- Full name
- Date of birth
- Government-issued ID numbers (passport, driver’s license, social security number)
- Login credentials & digital credentials
These identifiers allow users to access digital services securely. They include:
- Usernames
- Passwords
- PIN codes
- Security tokens
- Cryptographic keys
- Digital certificates
- Biometric identifiers
Biometrics use unique physical or behavioral traits to authenticate identity. Due to their convenience and security, biometrics are becoming increasingly popular.
- Fingerprints
- Facial recognition
- Iris scans
- Voice recognition
- Behavioral patterns like keystroke dynamics
- Device identifiers
Devices also have digital identities, which are used to track, authenticate, and secure online interactions.
- IP addresses
- MAC addresses
- Device fingerprints
- Unique mobile device IDs (like Apple’s Identifier for Advertisers - IDFA)
- Decentralized & blockchain-based identities
With growing concerns over privacy and security, decentralized identity systems are emerging. These allow individuals to control their credentials without relying on a single entity.
- Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
- Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
- Blockchain-based identity wallets
Digital identity use cases and examples
Digital identities are a cornerstone of modern life. From banking to healthcare, governments to social media, they help verify users, ease access to platforms, and prevent fraud.
1. Banking & finance: secure access to financial services
Banks and financial institutions rely on digital identities to verify customers and comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Usually, it’s used in online banking logins with biometric authentication (e.g., fingerprint or Face ID), for digital identity wallets storing verified KYC credentials for faster onboarding, and two-factor authentication (2FA) for securing financial transactions.
For example, many banks now support eKYC (electronic Know Your Customer), where you can open accounts remotely using biometric verification and document uploads instead of visiting a branch.
2. E-Government & public services: identity for citizens
Governments use digital identity systems to provide citizens with safe access to public services, which reduces bureaucracy and fraud. They utilize it for eID programs that let citizens file taxes, vote, or access healthcare, digital driver's licenses and passports stored in mobile wallets, or social security and pension systems that verify people through digital identity.
One such case is Estonia’s e-Residency program, which lets global entrepreneurs establish and run businesses digitally. The program offers a government-issued digital identity without requiring a physical presence.
3. E-Commerce & online services: personalized & fraud-free shopping
Online retailers use digital identities to personalize experiences, prevent fraud, and streamline checkout processes. Single Sign-On (SSO) for easy logins across e-commerce sites, fraud detection systems analyzing behavioral patterns to flag suspicious transactions, and digital wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay verifying users for contactless payments are just a few of many such examples.
Amazon’s palm-scanning payment system uses such a system to allow customers to link their palm signature to their payment method, which enables biometric checkouts in seconds.
4. Social media & entertainment: managing online presence
Social media platforms are known for relying on digital identities to verify users, manage accounts, and reduce fake profiles. Usually, they use AI-driven identity verification for content creators and influencers, and parental controls and age verification systems for streaming services.
TikTok’s age verification system uses AI to estimate a user’s age and prevent underage access to certain content.
5. Travel & transportation: digital passports for fast check-ins
Airlines, railways, and ride-sharing platforms use digital identities more and more in order to improve security and experience for their passengers. This includes biometric e-gates at airports for passport-free boarding, digital driver’s licenses for renting cars or verifying rideshare drivers, and secure ticketing systems tied to digital identities for public transportation.
One such case is Delta Air Lines’ facial recognition boarding system, which allows passengers to go through security and board flights without showing their physical passports or boarding passes.
Digital identity and security
As digital identities become more set in daily life, security becomes an increasing concern. Cybercriminals continue to find new ways to exploit weak authentication, steal credentials, and commit identity fraud. A compromised digital identity can lead to financial loss, data breaches, or unauthorized access to sensitive accounts.
Strong security measures are essential for protecting digital identities, starting with authentication, authorization, and identity management.
What is authentication?
Authentication is the process of verifying that someone is who they claim to be before granting access to a system or service. It acts as the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Successful, strong authentication combines three things:
- Something you know. This includes passwords, PIN codes, and security questions.
- Something you have. One-time passcodes (OTP), smart cards, or security tokens are typically used in this step.
- Something you are. Biometrics like fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans are utilized to verify that you are who you say you are.
Suggested read: 5 User Authentication Methods to Prevent Fraud in 2025
Authentication vs authorization
Authentication and authorization are often confused, but they serve different purposes in security.
| Factor | Authentication | Authorization |
| Definition | Verifies who you are | Determines what you can do |
| Example | Logging in with a password | Accessing specific files after logging in |
| When it happens | Before granting access | After authentication is successful |
For example, when signing into a corporate network, authentication checks your identity using a password and your biometrics. Once logged in, authorization determines what resources (files, applications) you can access based on your role.
What is Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework of policies and technologies that makes sure that the right individuals have appropriate access to resources at the right time. Organizations use IAM to control user identities, enforce security policies, and manage permissions. It has four main components:
- Authentication. Verifies user identity before granting access.
- Authorization. Determines what users can do once authenticated.
- Administration. Manages user identities, roles, and access controls.
- Auditing and reporting. Tracks and logs access activities for security and compliance.
Apart from that, IAM uses advanced tools like Single Sign-On (SSO), Multifactor Authentication (MFA), and Identity Governance and Administration (IGA) to make security and user experience better.
Privacy risks & considerations
Every login, transaction, or data submission contributes to your digital footprint, which, if mismanaged, can lead to identity theft, data breaches, and unauthorized surveillance. Protecting digital identities requires a careful balance between security, convenience, and privacy.
If not adequately protected, you risk a lot of potential privacy breaches. Hackers target identity databases to steal personal information (e.g., names, passwords, biometrics). Companies and governments collect massive amounts of identity data, often tracking users without explicit consent. Many users don’t fully control how their data is stored, shared, or deleted, and using weak passwords or reusing credentials for multiple platforms increases the risk of credential-stuffing attacks. Additionally, fraudsters impersonate trusted entities to trick users into revealing their credentials.
There are many considerations and practices you can use to avoid your privacy being put at risk:
- Decentralized identity solutions
- Look for data minimization & anonymization
- Check user consent & transparency
- Use privacy-enhancing authentication (eg. passwordless authentication)
- Use platforms with regular security audits & compliance checks
How is digital identity verified?
Digital identity verification involves confirming that a person is who they claim to be, typically through:
- Document verification. Assessing government-issued IDs or other official documents.
- Biometric verification. Using unique biological traits like fingerprints or facial recognition like Liveness.
- Knowledge-based verification. Asking security questions based on personal information.
- Two-factor authentication (2FA). Combining something the user knows (password) with something they have (a mobile device) or something they are (biometric data).
Trends & future challenges
Digital identity is rapidly evolving, influenced by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and societal needs. In July 2024, the European Union launched the first eIDAS-Testbed in collaboration with German tech firms in order to improve cross-border digital identification within the EU. Another similar improvement is China's blockchain-based RealDID system, introduced in December 2023, which facilitates real-name identity verification while maintaining user anonymity. As we move through 2025, several trends and challenges have emerged:
- Transition to digital credentials. The UK plans to introduce digital driving licenses accessible via a government app in 2025. These digital credentials will serve as proof of identity for various purposes, including purchasing alcohol, domestic flights, and voting. Similarly, countries like Finland, Canada, and Singapore are trialing paperless travel systems using facial recognition technology and digital travel credentials.
- Reusable identity. Reusable identity is perhaps the most prominent future trend of digital identity. Traditional identity verification is often repetitive, time-consuming, and privacy-invasive. Reusable identity solutions reduce verification time, improve security, and give users greater control over their data.
These emerging trends, naturally, bring a lot of challenges with them as well.
Centralizing personal information in digital wallets increases the risk of hacking and fraud. Cybersecurity experts warn that storing large volumes of personal data in one place could lead to identity theft and financial harm if breaches occur.
Also, as different countries and regions develop their digital identity systems, compatibility between them becomes a significant challenge. There is also a shift towards digital identities that may marginalize those without access to necessary technologies or digital literacy, which could only worsen already existing inequalities.
Addressing these challenges needs a collaborative approach involving governments, technology providers, and society to develop secure, inclusive, and user-centric digital identity solutions.
How can Sumsub help?
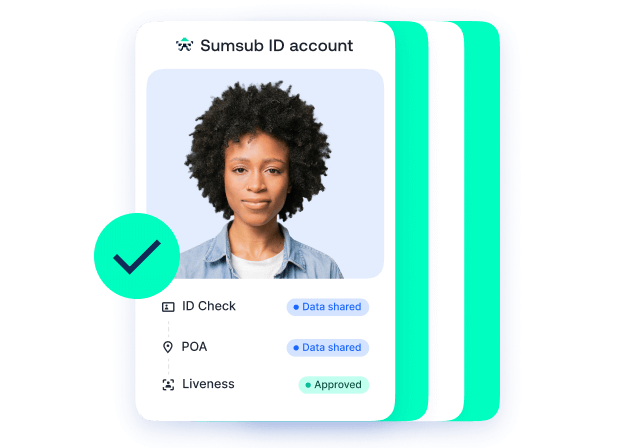
Managing digital identities safely and efficiently is an ever-present challenge for businesses and individuals alike as technology develops. Sumsub ID offers a secure solution for personal documents and data storage.
Sumsub ID enables users going through verification flows to store, access, and quickly share their document data wherever they verify through Sumsub. This means a more efficient verification experience and higher conversion rates, whether you’re a platform user or a business.
Sumsub verifies more than a million users per day for its clients, with an ever-expanding pool of Sumsub ID accounts. So, why use it?
- Higher converting verifications. Users can share previously stored documents with one click, which makes the process much smoother—and gives a 30% conversion improvement when using stored documents from Sumsub ID.
- Compliance. Sumsub will always perform relevant checks from your verification flow to ensure compliance. Using Sumsub ID simplifies and speeds up the process of uploading valid documents.
- Data privacy. Sumsub ID is designed with data privacy in mind, including GDPR compliance. Users retain complete control over when and how their document data is shared.
Sumsub ID protects users’ sensitive information, ensuring document data is safe from unauthorized access. To access Sumsub ID accounts or share data, users must verify their email address and pass a Liveness check.
Additionally, users will only be prompted to provide document data needed for a specific verification process, and they will always be asked to give explicit permission before any of their data is shared.
With Sumsub ID, businesses can significantly improve the verification flow experience by enabling users to store and reuse documents. This means no manual uploads and a much faster process, with a better UX.
-
How does digital identity affect access control?
Digital identity can determine who can access specific systems, data, or services by verifying user credentials and enforcing security policies like authentication and authorization.
-
What are common examples of digital identity?
Examples include government-issued eIDs, biometric data (fingerprints, facial recognition), social media profiles, email addresses, and digital wallets.
-
How to choose a digital identity verification service?
Look for a provider with strong security measures, compliance with global regulations (e.g., GDPR, KYC/AML), seamless user experience, and support for multiple verification methods like biometrics and document checks.
Relevant articles
- Article
- 2 weeks ago
- 6 min read
What counts as proof of address in the UK? See accepted documents and how to open a bank account if you’ve just moved to the country.
- Article
- Feb 3, 2026
- 11 min read
Arbitrage in Sports Betting & Gambling in 2026. Learn how iGaming businesses detect arbers using KYC & fraud prevention tools.

What is Sumsub anyway?
Not everyone loves compliance—but we do. Sumsub helps businesses verify users, prevent fraud, and meet regulatory requirements anywhere in the world, without compromises. From neobanks to mobility apps, we make sure honest users get in, and bad actors stay out.