- Mar 13, 2022
- 3 min read
Identification, Verification, and Authentication—What's the Difference?
People go through either identification, verification, or authentication on a daily basis—whether it’s opening a bank account, making online transactions, or creating a new social media profile. It can be hard to tell the differences between these three processes at first, but failing to understand them can land businesses in hot water. To keep businesses safe and compliant, this article clarifies these subtle, yet important differences.
What is identification?
Identification is the process of recognizing one’s claim to be a particular person. Regulations oblige financial companies to identify their customers, which often requires collecting certain information. JMLSG GUIDANCE FOR THE UK FINANCIAL SECTOR states that “the firm should obtain the following information in relation to the private individual”:
- full name;
- residential address;
- date of birth.
For in-person transactions, customers can identify themselves by simply stating their name. A similar identification process occurs during online transactions—where customers provide their email address in addition to their full name.
When occasional transactions don’t exceed a certain amount (e.g., 1.000 euro), businesses may allow their customers to complete them right after the identification process.
What is verification?
Verification is the process of ensuring that the information provided by customers during identification is authentic. This is necessary to avoid fraud, identity theft, and other illegal activities.
Identifying vs verifying
There’s a functional difference between verification and identification. If the identification process simply asks customers who they are, the verification process asks them to actually prove their identity and provide supporting documents. The verification stage is crucial since fraudsters can easily get their hands on identification data.
The verification process commonly takes place in higher-risk onboarding scenarios, such as online banking or betting. In these cases, it’s especially important to truly Know Your Customer before establishing the business relationship.
Document verification
Verification must be based on reliable sources that are independent of the customer. In other words, customers need to present legit documents to prove they are who they say they are. To ensure a high level of confidence, these documents should typically be issued by a government department or agency.
According to JMLSG GUIDANCE FOR THE UK FINANCIAL SECTOR, the verification process takes place by submitting one of the following government-issued documents:
- valid passport;
- valid photocard driving license (full or provisional);
- national Identity card;
- firearms certificate or shotgun license;
- identity card issued by the Electoral Office for Northern Ireland.
In cases when a document doesn’t include a photograph, a supporting document is required. Documents without a photograph include:
- valid (old style) full UK driving license;
- recent evidence of entitlement to a state or local authority-funded benefit (including housing benefit and council tax benefit), tax credit, pension, educational or other grants;
- instrument of a court appointment (such as liquidator or grant of probate);
- current council tax demand letter or statement.
The documents then get examined using two methods:
- identity checking compares the personal information on provided documents with what’s provided during the identification process.
- identity verification analyzes provided documents for the presence of specific watermarks, stamps, fonts, and holograms;
These examinations are conducted either manually or through computer technologies. Companies should decide which approach is appropriate depending on their business model. For companies with an intense flow of customers, the verification process will require a lot of resources, especially for non-face-to-face services. Therefore, such businesses tend to use special tools and services for remote identification and verification.
What is authentication?
If verification is a one-time process that takes place during the onboarding process, authentication is a recurring procedure that ensures that existing accounts haven’t been compromised. The three common types of authentication include:
- something that the user knows: secret questions;
- something that the user has: a mobile phone;
- something that the user is: biometric data.
The most common form of authentication is asking for the user's password. However, this information can easily be stolen by fraudsters. Therefore, the more types of authentication a business uses, the higher the chances that the fraudster won’t get access to the user’s accounts. Biometric data and liveness checks may have the highest information security levels, since they’re the most difficult to forge.
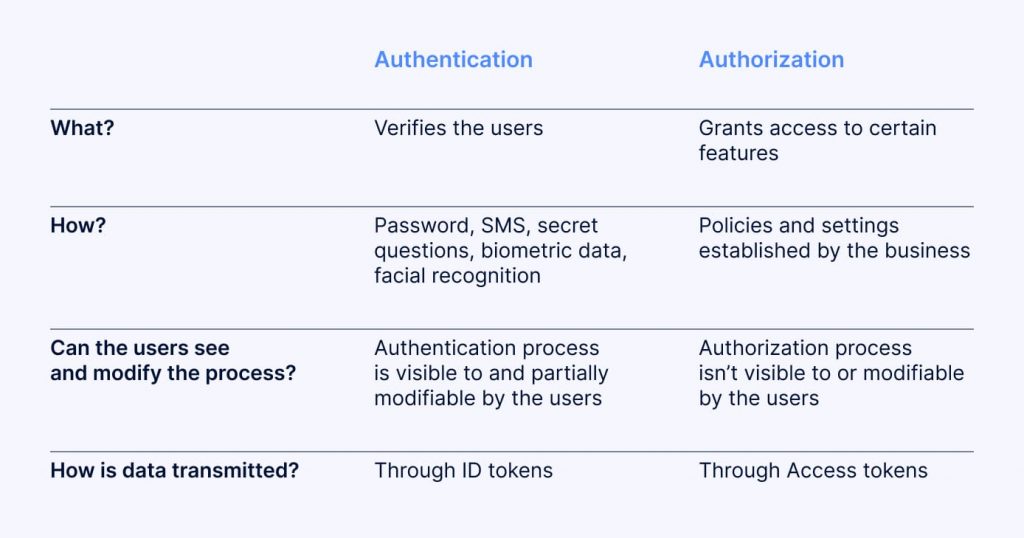
Authentication vs Authorization
“Authentication” often gets confused with another term called “authorization.” However, the difference between them is significant. Authentication aims to recognize users, while authorization specifies the features that users can access. For example, if a person is subscribed to a certain streaming service, authentication will recognize the subscriber, while authorization determines which features are available based on the subscription type.
How to protect your business
The main goal of identification, verification and authentication is to know your customers, protect your business from fraudsters, and comply with regulations. The best way to achieve these goals is to conduct all three processes simultaneously and combine different verification and authentication methods. To put it simply: the more, the merrier.
Relevant articles
- Article
- 3 days ago
- 11 min read
Check out how AI deepfakes are evolving and discover proven strategies for detecting and preventing deepfake threats to protect your business.

- Article
- 3 weeks ago
- 8 min read
Digital trust is transforming Asia's digital economy in 2026. Explore trends in superapps, data sovereignty, IDV, and AI fraud prevention.

What is Sumsub anyway?
Not everyone loves compliance—but we do. Sumsub helps businesses verify users, prevent fraud, and meet regulatory requirements anywhere in the world, without compromises. From neobanks to mobility apps, we make sure honest users get in, and bad actors stay out.